As climate concerns move from headlines into everyday decision-making, homeowners and businesses in cold regions are increasingly asking one important question: How can we heat our buildings without damaging the environment? In that conversation, geothermal stands out as one of the most effective answers.
Geothermal Heating Reduce strategies are gaining attention because they address two challenges at once—extreme cold and high carbon emissions. Unlike traditional heating systems that burn fuel, geothermal uses the earth’s natural, stable temperature to provide reliable warmth with dramatically lower emissions.
In this article, we’ll explore how Geothermal Heating Reduce carbon output in cold climates, why it works so well in harsh winters, and how it fits into the future of sustainable heating.
Why Heating Is a Major Source of Carbon Emissions
In cold climates, heating accounts for a large share of household and commercial energy use. Long winters mean heating systems run for months at a time, often relying on fossil fuels such as natural gas, oil, or propane.
These systems:
- Burn fuel directly on-site
- Release carbon dioxide and other pollutants
- Become less efficient during extreme cold
As a result, heating is often the largest contributor to a building’s geothermal heating carbon footprint comparison when measured against cleaner alternatives.
This is where geothermal offers a powerful shift.
How Geothermal Heating Works Differently
To understand how Geothermal Heating Reduce emissions, it’s important to understand how the technology works.
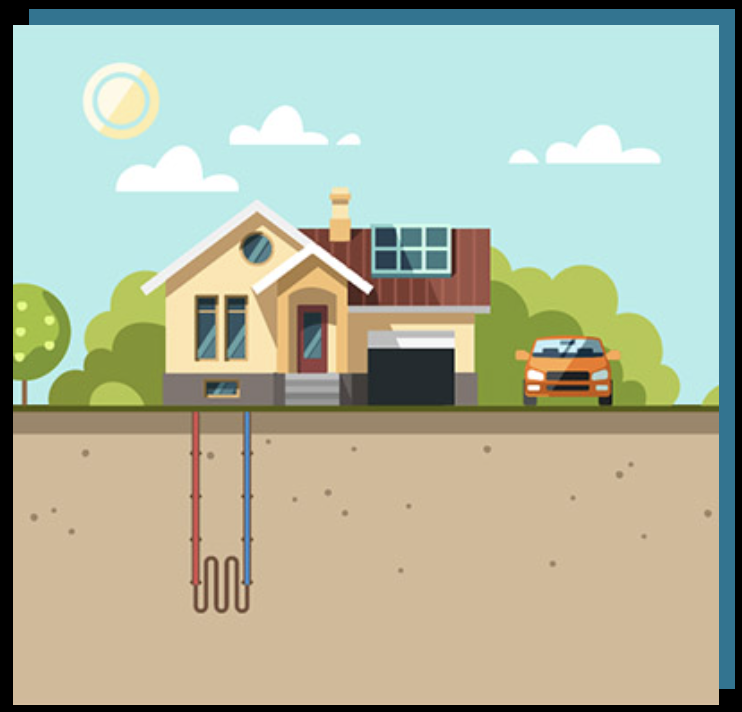
Geothermal systems don’t generate heat through combustion. Instead, they transfer heat.
Using underground pipes called ground loops, geothermal systems:
- Absorb heat stored in the earth during winter
- Move that heat indoors using a heat pump
- Reverse the process in summer for cooling
Because the ground maintains a stable temperature year-round, geothermal systems operate efficiently even during extreme cold.
Why Cold Climates Benefit the Most from Geothermal
It may seem counterintuitive, but colder regions often see the greatest environmental benefits from geothermal.
In cold climates:
- Heating demand is high
- Fossil fuel consumption is continuous
- Efficiency losses in conventional systems are common
A geothermal system avoids these issues entirely. Geothermal Heating Reduce emissions most dramatically where heating loads are highest, making it ideal for northern regions.
This is why geothermal is increasingly recognized as one of the most effective renewable heating for cold regions.
Geothermal Heating Reduce Carbon Emissions at the Source
Traditional heating systems emit carbon directly at the building. Geothermal systems do not.
Key reasons Geothermal Heating Reduce carbon footprint include:
- No on-site fuel combustion
- Electricity-based operation
- Extremely high efficiency ratios
Even when powered by a grid that still includes fossil fuels, geothermal produces significantly fewer emissions because it uses much less energy overall.
As grids continue to decarbonize, geothermal systems become even cleaner over time.
Ground Source Heat Pumps Efficiency Explained
One of the biggest reasons Geothermal Heating Reduce emissions is efficiency.
Ground source heat pumps efficiency is measured using Coefficient of Performance (COP). Many geothermal systems achieve:
- COP values of 3.5 to 5.0
- Meaning 3–5 units of heat for every unit of electricity used
By comparison:
- Gas furnaces max out near 95% efficiency
- Electric resistance heating delivers only 1:1 energy output
Higher efficiency directly translates into lower emissions.
Comparing Geothermal to Conventional Heating Systems
Let’s look at how Geothermal Heating Reduce carbon output compared to other systems.
Natural Gas Heating
- Burns fossil fuel directly
- Emits CO₂ and methane
- Efficiency drops in extreme cold
Oil and Propane Systems
- Higher emissions per unit of heat
- Fuel delivery and storage risks
- Volatile pricing
Electric Resistance Heating
- No on-site emissions
- Very high electricity demand
Geothermal Heating
- No combustion
- Minimal electricity use
- Stable performance year-round
This comparison clearly shows why geothermal is considered one of the most effective low-carbon heating systems available today.
Geothermal Heating Reduce Emissions Over System Lifetime
Short-term emissions matter, but long-term impact matters more.
A geothermal system typically lasts:
- 25+ years for indoor components
- 50+ years for ground loops
Over its lifetime, Geothermal Heating Reduce carbon emissions by tens of tonnes compared to fossil fuel systems. This cumulative impact is one of geothermal’s strongest environmental advantages.
The Role of Electricity in Carbon Reduction
Some people worry that geothermal still uses electricity. That’s true—but context matters.
Because Geothermal Heating Reduce overall energy demand so dramatically, even fossil-fuel-based electricity results in lower emissions than burning fuel directly.
Additionally:
- Renewable electricity continues to expand
- Solar and wind pair well with geothermal
- Future grid improvements further reduce impact
Geothermal is future-ready in a way combustion systems are not.
Low-Carbon Heating Systems and Climate Goals
Governments and municipalities worldwide are setting aggressive carbon reduction targets. Heating systems are a major focus.
Low-carbon heating systems like geothermal:
- Align with net-zero strategies
- Reduce reliance on imported fuels
- Support long-term energy resilience
This makes geothermal not just a personal sustainability choice, but a systemic solution.
Geothermal Heating Reduce Indoor and Local Pollution
Carbon dioxide isn’t the only concern.
Traditional heating systems also release:
- Nitrogen oxides
- Carbon monoxide
- Particulate matter
Geothermal systems eliminate on-site emissions entirely, improving:
- Indoor air quality
- Outdoor air quality
- Overall public health
These benefits are especially valuable in densely populated or cold regions where heating runs continuously.
Sustainable Heating Solutions Beyond Carbon
While emissions reduction is critical, sustainable heating solutions also consider long-term resource use.
Geothermal systems:
- Use renewable ground energy
- Require no fuel extraction
- Produce no waste byproducts
This makes geothermal one of the most complete sustainability solutions available for cold climates.
How Much Can Geothermal Reduce a Home’s Carbon Footprint?
While results vary, many homes see:
- 50%–80% reductions in heating-related emissions
- Even greater reductions when paired with renewable electricity
Over time, Geothermal Heating Reduce a home’s environmental impact more consistently than almost any other heating technology.
Geothermal in Extreme Cold: Reliability Matters
Environmental benefits only matter if a system works reliably.
Geothermal systems:
- Do not rely on outdoor air temperature
- Maintain stable performance during cold snaps
- Avoid efficiency drops seen in air-source systems
This reliability is crucial in cold climates, where heating failure isn’t just inconvenient—it’s dangerous.
Installation Quality Affects Carbon Savings
Not all geothermal systems are equal.
For Geothermal Heating Reduce emissions effectively, systems must be:
- Properly sized
- Correctly designed for soil conditions
- Professionally installed
A poorly designed system won’t reach its efficiency potential, reducing both savings and environmental benefits.
Why Geothermal Is a Long-Term Climate Investment
Unlike temporary efficiency upgrades, geothermal delivers benefits year after year.
Once installed:
- Emissions reductions continue automatically
- No behavior change is required
- Performance remains stable
This makes geothermal one of the most reliable long-term strategies to reduce carbon footprint in cold climates.
Frequently Asked Questions
How does geothermal heating reduce carbon footprint in cold climates?
Geothermal systems avoid fuel combustion and operate with very high efficiency. Geothermal Heating Reduce emissions by using renewable ground energy instead of burning fossil fuels, even during extreme cold.
Is geothermal heating considered a low-carbon heating system?
Yes. Geothermal is widely recognized as one of the most effective low-carbon heating systems because it delivers more heat with less energy and produces no on-site emissions.
Does geothermal still reduce emissions if electricity comes from fossil fuels?
Yes. Because geothermal uses far less electricity than conventional heating uses fuel, Geothermal Heating Reduce overall emissions even on mixed or fossil-heavy power grids.
Ready to Lower Your Carbon Footprint with Geothermal?
If you’re serious about reducing emissions while maintaining comfort in a cold climate, geothermal is one of the most effective solutions available.
Envirotech Geothermal specializes in designing and installing high-performance geothermal systems built for cold regions. Our team can assess your property, explain your potential carbon savings, and guide you through the process from start to finish.



